Athlete's foot is one of the most common fungal skin infections.The skin between the toes and the bottom of the foot are often infected.The disease is caused by fungi of the genus Trichophyton and Candida.Upon contact with the epidermis, they begin to multiply actively.The result of their activity is peeling of the skin, cracks between the fingers and diaper rash.At a later stage, the disease affects the nails, they become dull, thickened, the edges begin to crumble and yellow streaks are noticeable.The disease can spread to the hands and large skin folds on the body.
Scratching the affected skin or minor injuries allow the fungus to penetrate deeper into the dermis layers.Thus, the infection spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body.In children and older people, fungal skin damage occurs in a more acute form and is more difficult to treat.This is due to the age-related characteristics of the immune system.
Stress is also a trigger for the development of mycosis.Fungal infection is resistant to adverse external factors and prefers warmth and moisture.Showers with disturbed water flow, saunas, old house shoes, rental shoes (skates, roller skates, ski boots), fluffy carpets in bathrooms are the main breeding grounds for fungi.They penetrate the skin through scratches and calluses.
People with excessive sweating of the feet are at risk because, with prolonged exposure, the sweat corrodes the skin and reduces its protective properties.People with an erased form of mycosis with light peeling of the skin and painless microcracks that can only be noticed by a doctor pose a particular danger to others.
Chronic mycosis of the skin of the feet and nail plates is often the cause of autoimmune allergic reactions, including the development of bronchial asthma.It is important to treat mycosis correctly without transforming it into a stable chronic form.
Symptoms
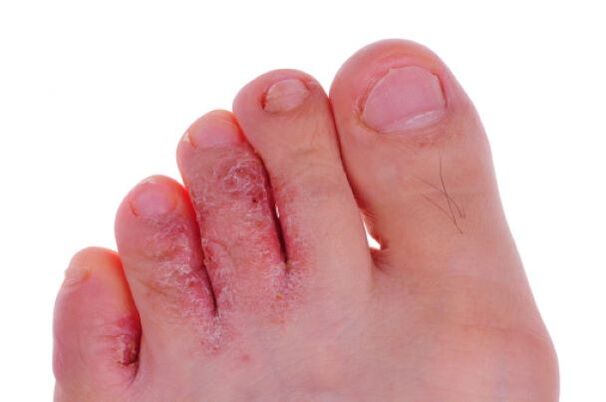
The symptoms of mycosis of the feet are very diverse.Initial symptoms: Cracks appear, painful or itchy blisters, diaper rash and roughening of the skin.Subsequently, the areas of the skin affected by the fungus soften, turn white and begin to peel.A bacterial infection can be added, after which the blisters transform into ulcers or sores.
Itching and burning are constant symptoms of mycosis, some patients complain of pain and an unpleasant smell.
Reasons
Athlete's foot is caused by several types of parasitic fungi.These microorganisms are present in large quantities on the floors of swimming pools and bathrooms, as well as in public showers.One can get infected by walking barefoot in such places.
Wearing other people's shoes, sharing towels and other personal care products is another common way to spread infection.
Immunity does not develop against fungal diseases, so re-infection occurs as easily as the initial one.
The reproduction of fungi is stimulated by improper foot hygiene: putting socks and shoes on wet feet, not washing socks daily and of poor quality, insufficient ventilation and drying of shoes.
The appearance of mycosis of the hands is mainly due to the action of fungal toxins circulating in the bloodstream.Also, when brushing the feet, microorganisms remain under the nails, from where they can be transferred to other parts of the body, incl.on the scalp.People susceptible to mycoses should always remember this route of infection.
Risk factors
Despite its rapid spread, not everyone develops athlete's foot.A strong and healthy body can handle a fungal infection on its own.However, it often happens that the immune system restrains the development of the fungus for a long time, after which stress, ARVI or another internal breakdown occurs and the fungal infection begins to progress rapidly.
It has been observed that people get sick more quickly under the following circumstances:
- profuse sweating;
- non-compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- hormonal imbalance;
- taking certain medications;
- frequent stress;
- chronic dermatological diseases.
Excessive sweating and neglecting the rules of personal hygiene create an ideal environment for the development of fungi.Sweat provokes the rapid reproduction of fungal microflora.Insufficient foot hygiene, socks made of synthetic fabric, too narrow and closed shoes accelerate the development and spread of the fungal infection.
Hormonal imbalance is common in adolescents, so they are at risk of developing ringworm.The restructuring of the hormonal system temporarily reduces immunity and can cause profuse sweating.These factors contribute to the growth and spread of pathogenic microflora.
A decrease in immunity may occur due to prolonged use of antibiotics and corticosteroids.
Ringworm, eczema, psoriasis and atopic dermatitis reduce cellular immunity and create favorable conditions for the addition of secondary infection, especially fungal.Mycosis is often a complication of dermatological diseases.Increase the risk of infection: shoes that are too tight;ingrown nails;abrasions and wounds on the legs;diabetes mellitus;vascular diseases.
Forms of the disease
Deleted form.Initial stage of the disease.Symptoms: slight peeling of the skin between the fingers, small cracks in the upper layer of the epidermis.The patient does not feel discomfort and may not suspect that he has mycosis.
Squamous form.The skin between the fingers peels and is covered with flat scales, with slight itching.
Hyperkeratotic form.Flat blue-red papules and plaques appear.The main localization of the lesion is the arch of the foot.The formations are covered with scales.The formation of individual bubbles is possible.The rash can merge into groups, forming large lesions.Over time, the entire foot is affected.Yellow hyperkeratotic formations (calluses) covered with cracks may appear.The skin is dry, with slight pain and itching.
Intertriginous form.The inflammation is similar to a common diaper rash.The greatest damage is observed on the skin between the fingers.A reddish swelling appears.Existing symptoms include ulcers and wetting.If left untreated, painful deep fissures and erosions occur.Patients note pain in the affected area, itching and severe burning.
Dyshidrotic form.Very dense bubbles.The localization of the lesions is the arches of the feet.The rash can spread, so prompt treatment is essential.If left untreated, the blisters spread over the entire surface of the foot, including the toes.Small blisters can coalesce into larger blisters that can burst.Reddish erosions remain in their place.
Sharp shape.Increased susceptibility to fungal pathogens and rapid disease progression.On the surface of the feet there is severe redness and swelling, large vesicles and blisters appear.After opening, large erosions develop in their place;the sores extend beyond the folds between the fingers.In some cases, weakness, fever and headache are noted.
Symptoms may vary from person to person.When the first alarming symptoms appear, you should consult a dermatologist.
Diagnosis of foot mycosis
Diagnosis and treatment of mycosis should be carried out by a dermatologist or mycologist.
Diagnosis includes:
- detailed examination of the foot;
- history taking;
- scraping from the affected areas of the skin or cutting off a piece of a deformed nail;
- a test to detect fungal infections in the body as a whole;
- seeding the material on a nutrient medium (if necessary);
- skin biopsy for analysis under a microscope (in rare cases);
- General and biochemical blood test.
Treatment
Improper or late treatment can lead to the development of mycosis in an advanced form.In this case, recovery can take up to six months or more.That is why you should seek help from a doctor at the first symptoms.First of all, it is necessary to accurately identify the pathogen;for this, the doctor takes a scraping from the affected skin.Based on the results, the optimal course of antifungal therapy is selected.Modern antifungal drugs - creams, gels, ointments, sprays - effectively cope with the disease.They have a wide range of action, are applied 1-2 times a day, do not stain the skin and underwear, and do not have a specific smell.
External means
The choice of drugs depends on the stage of mycosis.In mild forms, only external means are prescribed;in severe forms, systemic treatment is necessary.The most popular drugs for external use are terbinafine and naftifine.They act on a number of pathogenic fungi that cause mycosis of the feet.Do not cause side effects.Bifonazole and clotrimazole have a rapid action against yeast-like fungi.Thanks to their oily consistency, they effectively soften the skin and eliminate dryness, flaking and itching.These drugs speed up the healing and restoration process of the affected skin.Bifonazole is a complex drug aimed at treating foot and nail fungus.Eliminates itching, peeling, burning sensation and unpleasant odor.In addition to antifungal agents, it is important to regularly treat the skin with antiseptics.A solution of chlorhexidine or miramistin is good for this.When a secondary infection occurs and suppuration occurs, antibacterial ointments are prescribed.
Tablet drugs
For the treatment of mycosis of the feet: itraconazole, fluconazole, nystatin are used.For yeast-like fungi, fluconazole and nystatin are prescribed.The latter is considered an outdated drug and is rarely prescribed.Polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride granules are specially formulated to combat fungal infections of the feet.The scheme and duration of treatment are determined by the attending physician.
Recommendations
Athlete's foot is a fungal infection and the fungus only thrives in a moist environment.By eliminating moisture, you prevent the spread of infection.
Try to protect people around you from infection.Explain that you cannot walk barefoot in the apartment, especially in the bathroom.Every time after taking a shower, treat the bathtub or shower tray, as well as the bathroom floor with a disinfectant.
Every day before going to bed, wash your feet with plain soap and warm water, being careful not to make the skin too soft.Dry your feet thoroughly with a paper towel or hair dryer, paying special attention to the area between the toes.Don't forget to apply an antifungal cream or ointment.Continue treatment as recommended by your doctor, even if your symptoms have disappeared.Antifungal creams and ointments are only applied to dry skin.If your feet are prone to sweating, you should wait until the medicine is absorbed.
Wear cotton socks and wash them daily.When washing, use a chlorine bleach solution (not soap) or boil the socks for 10 minutes.This will remove the fungus from your clothes and prevent re-infection.Shoes should be disinfected with antifungal sprays and dried for several days (preferably in the sun).
Prevention of foot fungus
After you are outside, wash your hands thoroughly with soap.After being in one of the risk areas, wash your feet thoroughly with soap, dry with a towel and treat with an antifungal solution.If there is a person in the family with mycosis, he should have separate towels for his face, hands and feet.The bath should then be thoroughly treated with a special bath cleaner.If your feet sweat a lot, you can apply talcum powder or antiperspirant deodorant.Do not wear other people's shoes, especially slippers offered by guests, and in turn do not offer your shoes to others.
Try not to let your feet sweat.In a room where you will be staying for more than an hour, try changing your shoes with spare shoes.When visiting the sauna, public shower, swimming pool, wear rubber slippers, do not walk barefoot in public places.After showering, swimming in a lake or pool, treat your feet with an antifungal cream.Wear clean socks and tights every day.Do not let others use your sponges, towels, manicure and pedicure supplies.They must be disinfected before use.
Clean the tub with detergent and use a strong stream of water before using it.Remove wooden footstools as well as fabric and sponge rugs from the bathroom.They retain moisture and can leave behind flakes of skin and bits of nail infected with fungus.Use either a special grill (covered with special enamel or plastic) or a rubber mat.
Moisture in the folds between the fingers softens the skin and facilitates the entry of fungal infections.Wipe the creases between your toes with a separate foot towel or blow dry them.According to statistics, mycoses are more common in people with flat feet.Therefore, wear comfortable, high-quality shoes with a heel no higher than 4 cm with a special orthopedic insole or a soft protrusion that supports the arch of the foot.
No matter how complete and competent the home care of the feet is, it is necessary to regularly perform podiatric care of the skin of the feet and nail plates (medical pedicure).It will help to maintain healthy feet and nails, and the doctor will give individual recommendations for home care and prevention.
























